Introduction:
In Mesh analysis, we will consider the currents flowing through each mesh. Hence, Mesh analysis is also called as Mesh-current method.
A branch is a path that joins two nodes and it contains a circuit element. If a branch belongs to only one mesh, then the branch current will be equal to mesh current. If a branch is common to two meshes, then the branch current will be equal to the sum (or difference) of two mesh currents, when they are in same (or opposite) direction.
Procedure of Mesh Analysis:
Follow these steps while solving any electrical network or circuit using Mesh analysis.
Step 1 − Identify the meshes and label the mesh currents in either clockwise or anti-clockwise direction.
Step 2 − Observe the amount of current that flows through each element in terms of mesh currents.
Step 3 − Write mesh equations to all meshes. Mesh equation is obtained by applying KVL first and then Ohm’s law.
Step 4 − Solve the mesh equations obtained in Step 3 in order to get the mesh currents.
Now, we can find the current flowing through any element and the voltage across any element that is present in the given network by using mesh currents.
Example:
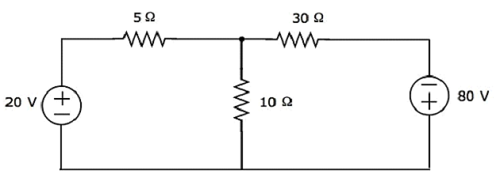
Find the voltage across 30 Ω resistor using Mesh analysis.
Step 1 − There are two meshes in the above circuit. The mesh currents I1 and I2 are considered in clockwise direction. These mesh currents are shown in the following figure.
Step 2 − The mesh current I1 flows through 20V voltage source and 5Ω resistor. Similarly, the mesh current I2 flows through 30Ω resistor and 80V voltage source. But, the difference of two mesh currents I1 and I2 flows through 10Ω resistor, since it is the common branch of two meshes.
Step 3 − In this case, we will get two mesh equations since there are two meshes in the given circuit. When we write the mesh equations, assume the mesh current of that particular mesh as greater than all other mesh currents of the circuit.
The mesh equation of first mesh is
5
I1 +10(I1 - I2) = 20
5I1
+ 10I1 -10I2 = 20
15I1 – 10I2 = 20
Divide the above equation with 5
3I1
– 2I2 = 4 -------------------- (1)
The mesh equation of second mesh is
10(I2
– I1) + 30I2 = 80
10I2
– 10I2 + 30I2 = 80
-10I1
+ 40I2 = 80
Divide the above equation with 10
-I1
+ 4I2 = 8 ------------------(2)
Step 4 − Finding mesh currents I1 and I2 by solving Equation 1 and Equation 2.
3I1 – 2I2 = 4 ----------------- (1)
-I1 + 4I2 = 8 ------------------(2)
(1) × 1 ⇒ 3I1 – 2I2 = 4
(2) × 3 ⇒ -3I1 + 12I2 = 24
(1) + (2) ⇒ 10I2 = 28
I2 = 2.8A
Substitute I2 = 2.8A in Equation 2.
3I1 – 2(2.8) = 4
3I1 – 5.6 = 4
3I1 = 4 + 5.6
3I1 = 9.6
So, we got the mesh currents I1 = 3.2A and I2 = 2.8A respectively.
Step 5 − The current flowing through 30Ω resistor is nothing but the mesh current I2 and it is equal to 2.8A. Now, we can find the voltage across 30Ω resistor by using Ohm’s law.
V30Ω = I2 R
V30Ω = 2.8
× 30
V30Ω = 84V
Therefore, the voltage across 30 Ω resistor of the given circuit is 84 V.

Comments
Post a Comment